
Python Socket Client Server Code The String
Writer.write(data) await writer.drain() print(Close the client socket).In the following code, the server sends the current time string to the client:Also, we will create our own client/server program to create a remote calculator. Connect Python Server And Java Client.Simplest way to write an async client server (like with that python library). Import Library : import jpysocket. Remove Package : pip uninstall jpysocket. Installation : pip install jpysocket. Decode The String Received From Java Socket And Encode The String for Send To The Java Socket Connect Python And Java Sockets Send And Recieveing The Data Beetween Java And Python Sockets.
Socket helps in the communication of two. Sockets are just the endpoints of a two-way communication link in a network. Those more familiar with Java might find this client-server tutorial more useful.
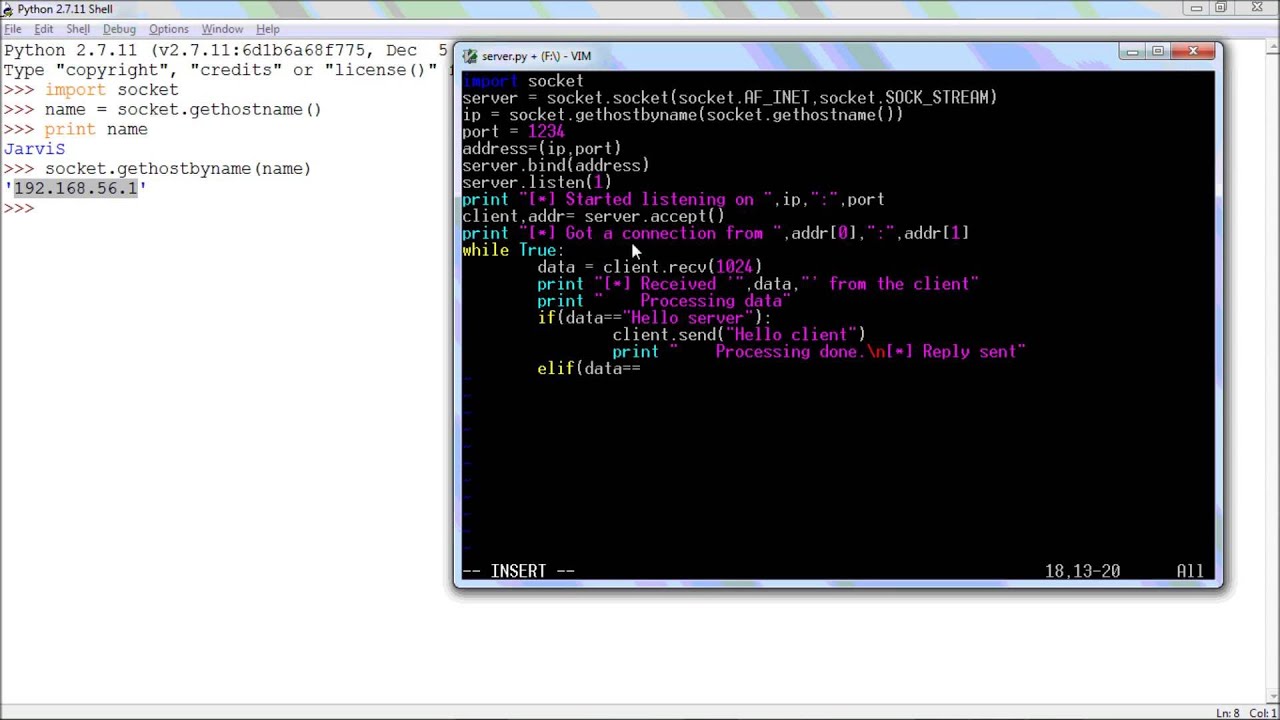
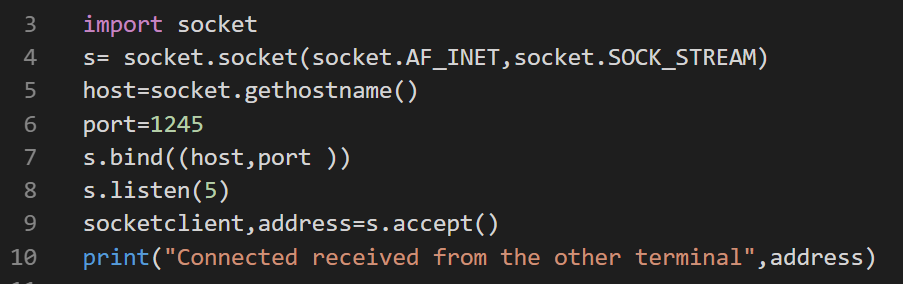
socket.bind(address): Bind the socket to address. socket.socket(): Create a new socket using the given address family, socket type and protocol number. Accept()Print("Got a connection from %s" % str(addr))CurrentTime = time.ctime(time.time()) + "\r\n"Clientsocket.send(currentTime.encode('ascii'))Here is the summary of the key functions from socket - Low-level networking interface: Launch the server program, Figure 10-7 shows the client's anticipated output.Clientsocket,addr = serversocket.
socket.send(bytes): Send data to the socket. This allows a server to manage connections from a large number of clients simultaneously. In particular, the accept() system call returns a new socket object that's actually used for the connection. This new socket is used solely for communication with this particular client.For TCP servers, the socket object used to receive connections is not the same socket used to perform subsequent communication with the client. socket.accept(): The return value is a pair (conn, address) where conn is a new socket object usable to send and receive data on the connection, and address is the address bound to the socket on the other end of the connection.At accept(), a new socket is created that is distinct from the named socket. The backlog argument specifies the maximum number of queued connections and should be at least 0 the maximum value is system-dependent (usually 5), the minimum value is forced to 0.
Sockets are automatically closed when they are garbage-collected, but it is recommended to close() them explicitly.Note that the server socket doesn't receive any data. The remote end will receive no more data (after queued data is flushed). All future operations on the socket object will fail. socket.colse(): Mark the socket closed. Applications are responsible for checking that all data has been sent if only some of the data was transmitted, the application needs to attempt delivery of the remaining data. Returns the number of bytes sent.
Socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)Print("The time got from the server is %s" % tm.decode('ascii'))The output from the run should look like this:Got a connection from ('127.0.0.1', 54597)The time got from the server is Wed Jan 29 19:14:15 2014"If you need fast IPC between two processes on one machine, you should look into whatever form of shared memory the platform offers. As soon as we've created that clientsocket, we go back to listening for more connections.S = socket. Each clientsocket is created in response to some other client socket doing a connect() to the host and port we're bound to.
IPython and Jupyter - Install Jupyter, iPython Notebook, drawing with Matplotlib, and publishing it to GithubIPython and Jupyter Notebook with Embedded D3. Simple tool - Concatenating slides using FFmpeg. RabbitMQ(Message broker server) and Celery(Task queue). Fabric - streamlining the use of SSH for application deploymentAnsible Quick Preview - Setting up web servers with Nginx, configure enviroments, and deploy an AppNeural Networks with backpropagation for XOR using one hidden layerNLP - NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
